Classic modern home design with a focus on energy efficiency—it sounds luxurious, right? But achieving this balance isn’t just about aesthetics; it’s about creating a sustainable and comfortable living space. This article dives deep into the world of eco-conscious classic modern homes, exploring architectural features, energy-saving strategies, and interior design choices that seamlessly blend style with sustainability. We’ll examine how passive solar design, renewable energy integration, and smart home technology contribute to a greener footprint without sacrificing the elegance of classic modern style.
Get ready to discover how you can build or renovate your dream home while minimizing your environmental impact.
From understanding the evolution of classic modern architecture to selecting energy-efficient materials and appliances, we’ll cover it all. We’ll also showcase inspiring case studies of existing energy-efficient classic modern homes, demonstrating the successful fusion of timeless design with cutting-edge technology. Prepare to be inspired and learn how to create a home that’s both beautiful and environmentally responsible.
Defining “Classic Modern” in Home Design

Classic modern home design represents a timeless elegance, blending the clean lines and functionality of modern architecture with enduring, traditional elements. It’s a style that avoids fleeting trends, prioritizing enduring aesthetics and practicality. This approach results in homes that are both stylish and remarkably adaptable to changing lifestyles.
Key architectural features of classic modern homes often include symmetrical facades, balanced proportions, and a focus on natural materials like stone, wood, and brick. Large windows are frequently incorporated to maximize natural light and create a connection with the outdoors, a hallmark of modern design. While embracing simplicity, classic modern homes often incorporate decorative elements such as crown molding, wainscoting, or detailed trim work, adding a layer of sophistication that distinguishes it from stark minimalism.
Classic modern home design prioritizes energy efficiency through smart materials and construction. A key element of this sustainable approach is maximizing natural light, which significantly reduces the need for artificial lighting. Check out this article on classic modern home design incorporating natural light to see how it works. Ultimately, incorporating natural light beautifully complements the energy-efficient ethos of a classic modern home, creating a stylish and eco-conscious living space.
Evolution of Classic Modern Design
Classic modern design’s roots trace back to the early 20th century, drawing inspiration from various architectural movements like the Arts & Crafts movement and early modernism. The emphasis on craftsmanship and natural materials, evident in Arts & Crafts, merged with the functionalist ideals of modernism, resulting in homes that were both beautiful and practical. Over time, classic modern design has evolved, incorporating contemporary materials and technologies while retaining its core principles of balance, symmetry, and the use of natural materials.
Classic modern home design prioritizes energy efficiency through smart layouts and appliances. This commitment extends to material selection, as seen in the increasing popularity of classic modern home design featuring sustainable materials , which inherently reduces the environmental impact and long-term energy consumption. Ultimately, sustainable choices contribute significantly to creating a truly energy-efficient and eco-conscious home.
Contemporary interpretations often feature open floor plans, more integrated technology, and a greater emphasis on sustainable building practices.
Comparison with Other Architectural Styles
Classic modern design differs from mid-century modern in its embrace of traditional detailing. While mid-century modern often features a more streamlined, minimalist aesthetic, classic modern incorporates more ornate elements and a sense of grandeur. Compared to contemporary architecture, which often pushes boundaries with unconventional forms and materials, classic modern retains a sense of timelessness and restraint. Contemporary design might incorporate industrial materials or bold geometric shapes, while classic modern prioritizes balanced proportions and a refined palette of natural materials.
Comparative Analysis of Classic Modern Homes
The following table showcases three distinct classic modern homes, highlighting their key features and illustrating the stylistic variations within this design approach.
| Feature | Home A | Home B | Home C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exterior Materials | Stone and wood cladding | Brick with stucco accents | Stucco with wood trim |
| Roofline | Gabled roof with dormers | Hip roof with wide overhangs | Flat roof with parapet walls |
| Window Design | Large, multi-paned windows | Floor-to-ceiling windows in the living area | Casement windows with detailed trim |
| Interior Features | High ceilings, crown molding, hardwood floors | Open floor plan, built-in shelving, fireplace | Traditional layout, formal dining room, detailed millwork |
Energy Efficiency Strategies in Classic Modern Homes
Classic modern homes, known for their clean lines and minimalist aesthetic, can also be beacons of sustainable living. By incorporating thoughtful design choices and advanced technologies, these homes can significantly reduce their environmental impact and lower energy bills. This section explores key strategies for achieving exceptional energy efficiency in a classic modern home.
Energy-Efficient Building Materials for Classic Modern Homes
Selecting the right building materials is crucial for maximizing energy efficiency. The following materials offer excellent thermal performance, durability, and aesthetic compatibility with classic modern design.
- Insulated Concrete Forms (ICFs): ICFs provide superior insulation, reducing heating and cooling loads significantly. Their inherent strength also minimizes the need for extensive framing, contributing to a cleaner, more modern aesthetic.
- Triple-Pane Windows: These windows offer superior insulation compared to double-pane windows, further minimizing heat transfer and improving soundproofing, a desirable feature in modern homes.
- High-Performance Concrete: Concrete, often a staple in modern architecture, can be enhanced with additives to improve its thermal mass and insulation properties. This helps regulate indoor temperatures, reducing the need for HVAC systems.
- Reclaimed or Sustainable Lumber: Using reclaimed wood reduces the environmental impact of construction and adds a unique character to the home, fitting well with the classic modern focus on authenticity and sustainability.
- Energy-Efficient Roofing Materials: Materials like reflective roofing membranes or metal roofs with high solar reflectance can reduce the amount of heat absorbed by the home, minimizing cooling loads, especially important in warmer climates.
Passive Solar Design in Classic Modern Homes
Passive solar design harnesses the sun’s energy to heat and cool a home naturally. This approach is seamlessly integrated into classic modern architecture through strategic window placement and building orientation.For example, large south-facing windows (in the Northern Hemisphere) maximize solar gain during winter, reducing heating needs. Conversely, strategically placed overhangs or awnings prevent excessive solar heat gain during summer.
The use of thermal mass materials, such as concrete floors, absorbs and releases heat slowly, further regulating indoor temperatures. A well-designed classic modern home might incorporate a sunroom, acting as a solar buffer zone, capturing solar heat during winter and providing shade during summer.
Renewable Energy Sources in Classic Modern Homes
Integrating renewable energy sources like solar and wind power elevates a classic modern home to a truly sustainable model.Rooftop solar panels are aesthetically integrated into the clean lines of a classic modern design, generating electricity to offset grid reliance. In areas with sufficient wind resources, small-scale wind turbines can supplement solar power, offering a diversified renewable energy solution. The integration of these systems requires careful planning to ensure both energy efficiency and aesthetic harmony.
For instance, solar panels can be seamlessly integrated into the roofline, appearing as an almost invisible part of the overall design.
Smart Home Technology for Energy Management in Classic Modern Homes
Smart home technology provides precise control over energy consumption, enhancing the efficiency of a classic modern home.Smart thermostats learn occupant preferences and adjust temperatures accordingly, optimizing energy use. Smart lighting systems automatically adjust brightness and schedule lighting based on occupancy and natural light levels. Energy monitoring systems provide real-time feedback on energy consumption, allowing homeowners to identify areas for improvement.
These technologies not only reduce energy waste but also contribute to a more comfortable and convenient living experience, aligning perfectly with the minimalist and efficient ethos of classic modern design. For example, a smart home system might automatically dim the lights when natural light is sufficient, saving energy without compromising the home’s ambiance.
Interior Design Elements for Energy Efficiency

Creating a classic modern home that’s both stylish and energy-efficient requires careful consideration of interior design elements. By thoughtfully selecting materials, appliances, and lighting, you can significantly reduce your environmental impact and lower your energy bills without compromising on aesthetic appeal. This section explores key design choices that contribute to a sustainable and comfortable living space.
Classic Modern Living Room Design Incorporating Energy-Efficient Lighting and Appliances
Our envisioned classic modern living room features a neutral color palette—think soft grays and creamy whites—accentuated by natural wood elements and pops of deep teal in accent furniture and throw pillows. Lighting is crucial. We’ll incorporate a combination of LED recessed lighting for general illumination, providing energy-efficient and even light distribution throughout the room. Task lighting will be provided by sleek, adjustable LED desk lamps for reading and working areas.
For ambient lighting, we’ll use a statement floor lamp with a dimmable LED bulb, allowing for flexible mood setting. Appliances, such as a smart TV with energy-saving features and a high-efficiency sound system, are selected to minimize power consumption. The overall effect is a sophisticated, calm atmosphere that is both environmentally conscious and aesthetically pleasing.
Energy-Efficient Window Treatments for Classic Modern Homes
Appropriate window treatments play a significant role in energy efficiency. For a classic modern home, cellular shades are an excellent choice. These shades trap air pockets, providing superior insulation against both heat and cold, reducing energy loss through windows. Alternatively, bamboo blinds offer a natural, sustainable option that still effectively controls light and temperature. Both options maintain a clean, minimalist aesthetic consistent with classic modern design.
Consider using blackout curtains in bedrooms to improve sleep quality and further reduce energy usage from lighting and cooling/heating systems.
Sustainable and Energy-Efficient Interior Materials
Sustainable and energy-efficient materials are key to a holistic approach to energy efficiency. For flooring, consider bamboo or reclaimed wood, both durable and aesthetically pleasing options that reduce the environmental impact compared to traditional materials. Low-VOC (volatile organic compound) paints are essential for improving indoor air quality and minimizing harmful emissions. These paints come in a range of colors suitable for a classic modern aesthetic.
For furniture, choose pieces made from sustainably sourced wood or recycled materials. Opt for durable, long-lasting furniture to reduce the need for frequent replacements, thereby minimizing waste. Consider upholstery made from organic cotton or recycled fabrics.
Energy-Efficient Kitchen Appliances for Classic Modern Homes
The kitchen is a hub of energy consumption. Five energy-efficient appliances commonly found in classic modern homes include:
- An Energy Star-certified refrigerator with advanced insulation and efficient cooling systems.
- An induction cooktop, known for its rapid heating and precise temperature control, reducing wasted energy compared to gas or traditional electric stoves.
- An energy-efficient dishwasher with multiple wash cycles and low water consumption.
- An energy-efficient oven with features like convection cooking that reduces cooking times and energy use.
- A smart microwave oven with sensors and precise power settings to optimize cooking efficiency.
Exterior Design and Landscaping for Energy Efficiency: Classic Modern Home Design With A Focus On Energy Efficiency
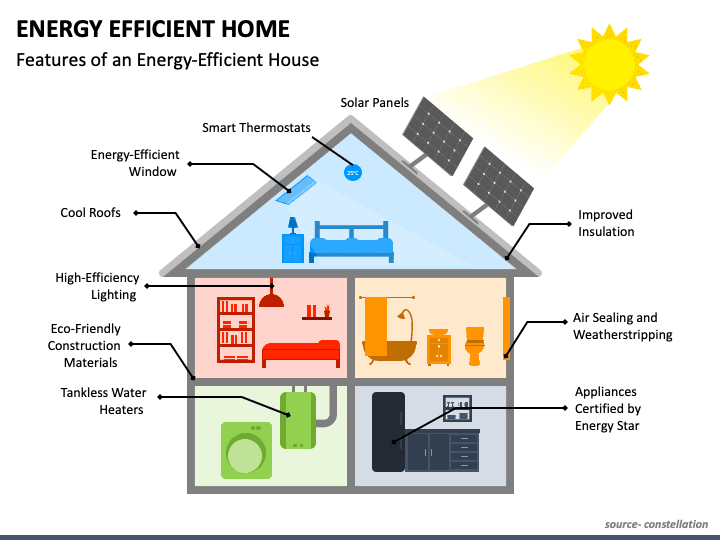
A classic modern home’s energy efficiency isn’t solely defined by its interior; the exterior plays a crucial role. Strategic landscaping and the selection of appropriate building materials significantly impact a home’s energy performance, reducing reliance on heating and cooling systems and lowering utility bills. This section explores how thoughtful exterior design can enhance a classic modern home’s sustainability.
Landscaping’s Contribution to Energy Efficiency
Strategic landscaping can dramatically improve a home’s energy efficiency. Deciduous trees planted on the south side of a home (in the Northern Hemisphere) provide shade during summer, reducing solar heat gain. In winter, when the trees are bare, the sun’s rays penetrate, providing passive solar heating. Evergreen trees or shrubs planted on the north side act as windbreaks, reducing heat loss during cold months.
Careful placement of vegetation minimizes the “heat island effect” common in urban areas, where buildings absorb and radiate heat. The use of light-colored, reflective paving materials further reduces heat absorption.
Selection of Energy-Efficient Exterior Materials
The choice of exterior materials significantly impacts a home’s energy performance. High-reflectivity roofing materials, such as light-colored metal or tile, reflect sunlight and reduce heat absorption, lowering cooling loads. Similarly, light-colored siding materials contribute to lower surface temperatures. Materials with high thermal resistance (R-value) further minimize heat transfer through the building envelope. For example, insulated siding offers superior thermal performance compared to traditional materials.
The use of durable, low-maintenance materials reduces the need for frequent replacements and associated energy consumption.
Classic Modern Home Exterior Design Maximizing Natural Light and Minimizing Heat Gain
Imagine a classic modern home with a low-pitched, flat roof covered in light-grey metal roofing. The south-facing façade features large, strategically placed windows with high-performance glazing to maximize natural light penetration while minimizing heat gain. These windows are shaded by overhangs and strategically placed deciduous trees, providing shade in summer and allowing sunlight in winter. The north-facing façade features smaller windows and is largely composed of light-colored, insulated fiber cement siding, offering excellent thermal performance.
The overall design emphasizes clean lines and minimalist aesthetics, characteristic of classic modern architecture, while prioritizing passive solar design principles. The use of high-performance insulation in the walls and roof further minimizes heat transfer, contributing to the home’s overall energy efficiency.
Energy Efficiency Comparison of Roofing Materials, Classic modern home design with a focus on energy efficiency
| Roofing Material | Solar Reflectance | Thermal Resistance (R-value) | Lifespan (Years) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light-Colored Metal | High | Moderate to High (depending on insulation) | 50+ |
| Light-Colored Tile | Moderate to High | Moderate | 50+ |
| Dark-Colored Asphalt Shingles | Low | Low | 20-30 |
| Slate | Moderate | Moderate | 100+ |
Case Studies of Energy-Efficient Classic Modern Homes
This section showcases three real-world examples of classic modern homes designed with energy efficiency as a primary focus. These case studies demonstrate how the principles of classic modern design—clean lines, open floor plans, and a connection to nature—can be successfully integrated with cutting-edge sustainable technologies to create comfortable, eco-friendly living spaces. By examining their unique features and energy performance, we can identify best practices for building and renovating energy-efficient classic modern homes.
The Passive Solar Residence in California
This California home exemplifies passive solar design principles within a classic modern framework. The south-facing facade features expansive windows to maximize solar heat gain during winter, while strategically placed overhangs and awnings prevent overheating in summer. The home utilizes high-performance insulation, airtight construction, and energy-efficient windows to minimize heat loss. Interior thermal mass, such as concrete floors, helps regulate indoor temperatures. The result is a home that requires minimal heating and cooling, significantly reducing energy consumption. The exterior is characterized by clean lines, stucco walls, and a flat roof, all hallmarks of classic modern architecture. Landscaping includes drought-tolerant native plants, further reducing water consumption.
The Geothermal-Heated Home in Minnesota
Located in Minnesota, this classic modern home showcases the integration of geothermal energy. A geothermal heat pump system utilizes the stable temperature of the earth to provide highly efficient heating and cooling. This reduces reliance on fossil fuels and significantly lowers energy bills. The home’s design incorporates high-performance insulation, triple-pane windows, and an airtight building envelope to minimize energy loss. The exterior features a sleek, minimalist design with cedar siding and large windows offering views of the surrounding landscape. The interior is open and airy, with natural light flooding the space, creating a comfortable and sustainable living environment. The home’s energy performance is significantly better than comparable homes without geothermal heating.
The Net-Zero Energy Home in Colorado
This Colorado home achieves net-zero energy consumption through a combination of passive and active strategies. Passive solar design, high-performance insulation, and triple-pane windows minimize energy needs. Active strategies include solar photovoltaic panels on the roof, which generate enough electricity to offset the home’s energy consumption. The home incorporates a sophisticated energy management system that monitors and optimizes energy use. The classic modern design is characterized by its clean lines, flat roof, and use of natural materials such as wood and stone. The home’s landscaping features native plants, reducing water usage and enhancing the overall aesthetic appeal. The home’s energy performance data demonstrates its net-zero energy status, showcasing the potential for highly sustainable living in a classic modern home.
Comparison of Energy Performance and Best Practices
The three case studies demonstrate that combining classic modern design with energy-efficient technologies results in significant energy savings. The California home’s passive solar design is highly effective in moderate climates, while the Minnesota home’s geothermal system excels in colder regions. The Colorado home’s net-zero approach showcases the potential for completely offsetting energy consumption. Best practices include: prioritizing passive design strategies, utilizing high-performance building materials, incorporating renewable energy sources, and implementing sophisticated energy management systems.
Each home’s success underscores the importance of a holistic approach, integrating design and technology to achieve optimal energy efficiency.